Mechanics & Industry. Volume 16, Number 7, 2015. WoS.
Abstract. This work describes a whole processing route for obtaining dense and nanostructured zirconia-nickel composites with low contents of metallic phase (1–3.5 vol%). For the processing route, a combination of spray-freezing and lyophilization has been proposed. After the calcination and reduction of the resulting powders an X-ray and HRTEM characterization has been performed. This showed the formation of pure zirconia and nickel, well dispersed and homogeneously distributed, nanostructured phases. The obtained powders were subsequently sintered by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). As a result, dense ZrO2-Ni composites were obtained, revealing that the sizes of the metal particles were kept in the nanometer range and appear homogeneously and well dispersed into the ceramic matrix. The mechanical behavior of these materials was evaluated by means of the Vickers hardness, showing and increment of about 25% with respect to pure zirconia with only a Ni concentration of 1 vol%.
Key words: Spark plasma sintering / nanomaterials / nanocomposites / nanoceramics / powder materials / zirconia-nickel composites / mechanical properties

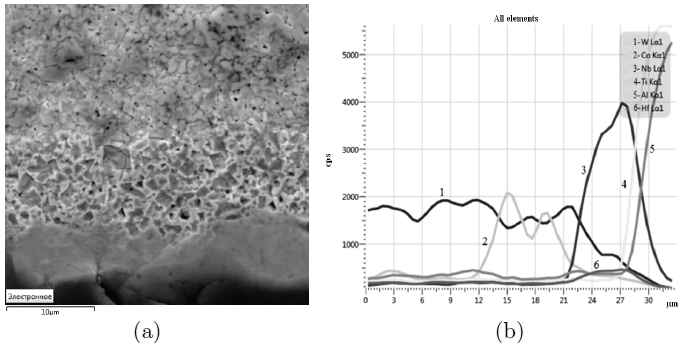
TEM micrograph of the 2.5 vol% Ni powder with the overlap EDX mapping showing the location of the Ni nanoparticles (a) and HRTEM micrograph of a Ni nanoparticle epitaxially grown on the surface of a zirconia particle. The interface between both particles presents an excellent matching of atomic planes (b).
Исполнители: Carlos F. Gutierrez-Gonzalez, Nestor W. Solis Pinargote, Said Agouram, Pavel Y. Peretyagin, Sonia Lopez-Esteban and Ramon Torrecillas
Дата публикации: 30-11-2015
Источник: https://www.mechanics-industry.org/articles/meca/abs/2015/07/mi150196/mi150196.html